温度补偿磁铁特别是指 钐钴磁铁 剩磁温度系数极低。
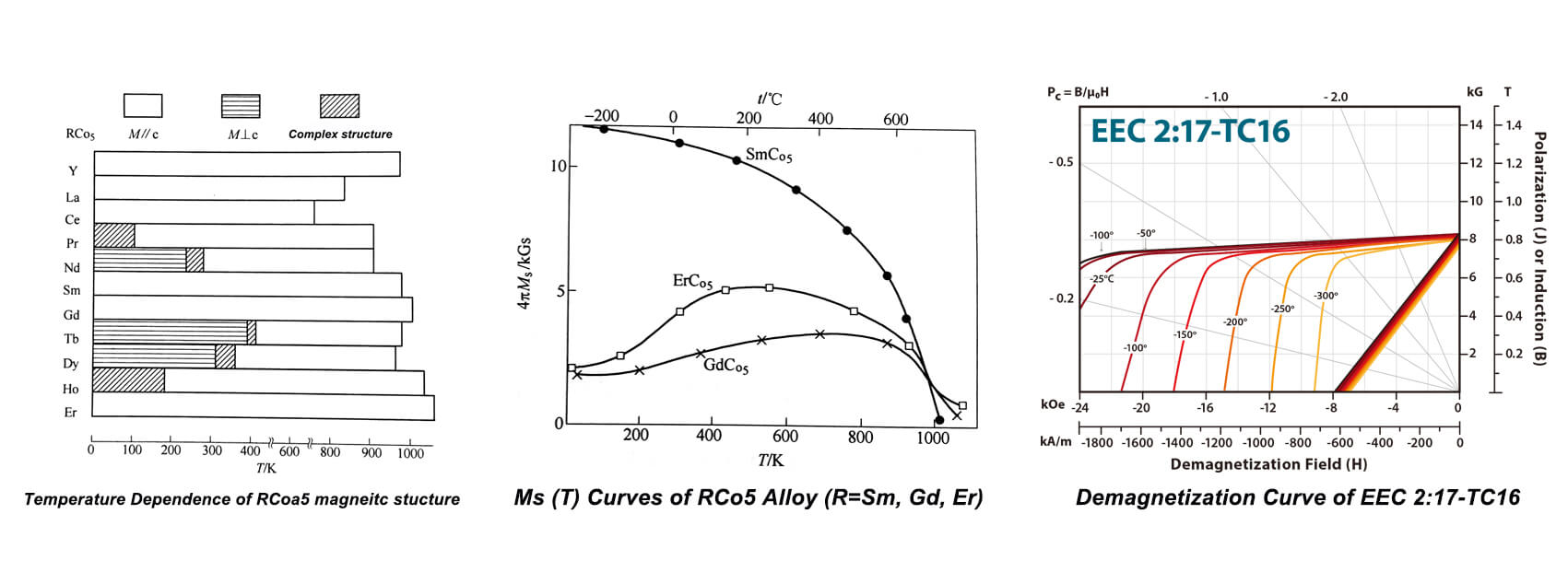
除了 铽 和 镝,RCo5 μ0Ha at room temperature of these compounds are all larger than 10T due to the strong uniaxial anisotropy of Cobalt's sublattice.由于钴的亚晶格具有很强的单轴各向异性,因此这些化合物在室温下都大于XNUMXT。 NdCo钕钴5 has spin reorientation transition at 280K.在XNUMXK处有自旋重取向转变。 Then its easy axis will deviate from c-axis and μ然后它的易轴将偏离c轴和μ0Ha 在室温下仅为0.5T。 因此,除钕,b和Dy以外的稀土元素可以替代mar的一部分构成(Sm,R)Co5 alloy with superior uniaxial anisotropy in principle.原则上具有优越的单轴各向异性的合金。 Even SmCo甚至S钴5 already have relatively low temperature coefficient of remanence, it still unable to fulfil the requirements of travelling wave tube, gravity sensor, and gyroscope in aerospace or precision instrument.已经具有较低的剩磁温度系数,它仍然不能满足航空航天或精密仪器中行波管,重力传感器和陀螺仪的要求。 In order to reduce low temperature coefficient of remanence to 0.02%/degree Celsius or even close to zero, magnet manufacturers must utilize ferrimagnetic coupling characteristics which generated by antiparallel arrangement of heavy rare earth's (HR) and Cobalt's atomic magnetic moment, thus decline of M为了将低温剩磁系数降低到XNUMX%/摄氏度甚至接近零,磁体制造商必须利用铁磁耦合特性,该特性是由重稀土(HR)和钴原子磁矩的反平行排列产生的,因此M的下降s (T)在S钴5 将由HRCo赔偿5。 中号s GdCo的(T)5 和ErCo5 随着温度的升高,温度分别在-150〜450和-270〜250摄氏度之间增加。 因此,用中度Ga或Er替代substitute可以制备(Sm,R)Co5 2:17型Sm2(Co,Cu,Fe,Zr)17 还可以通过引入中,重稀土元素来制备温度补偿磁体。